Quadriplegia: Causes, Symptoms And Care
Quadriplegia is a limiting condition, but with treatment and time it is possible to have a good quality of life and a wide margin of autonomy. In these cases, help and understanding of the environment is very significant.

Quadriplegia is a condition caused by injury or disease. Its consequence is the partial or total loss of movement and / or functionality in all four extremities and in the torso. It is also known as quadriplegia.
80% of tetraplegia cases affect men. Available data indicate that 50% of total cases are in people between 18 and 25 years of age. Most commonly, this condition is the result of a traffic accident among young people and a fall among older people.
Currently, there is no cure for quadriplegia. This type of paralysis affects the quality of life of those who suffer from it and is a risk condition for developing other health problems. Proper treatment can help solve the problem to some extent.
How does the central nervous system work?
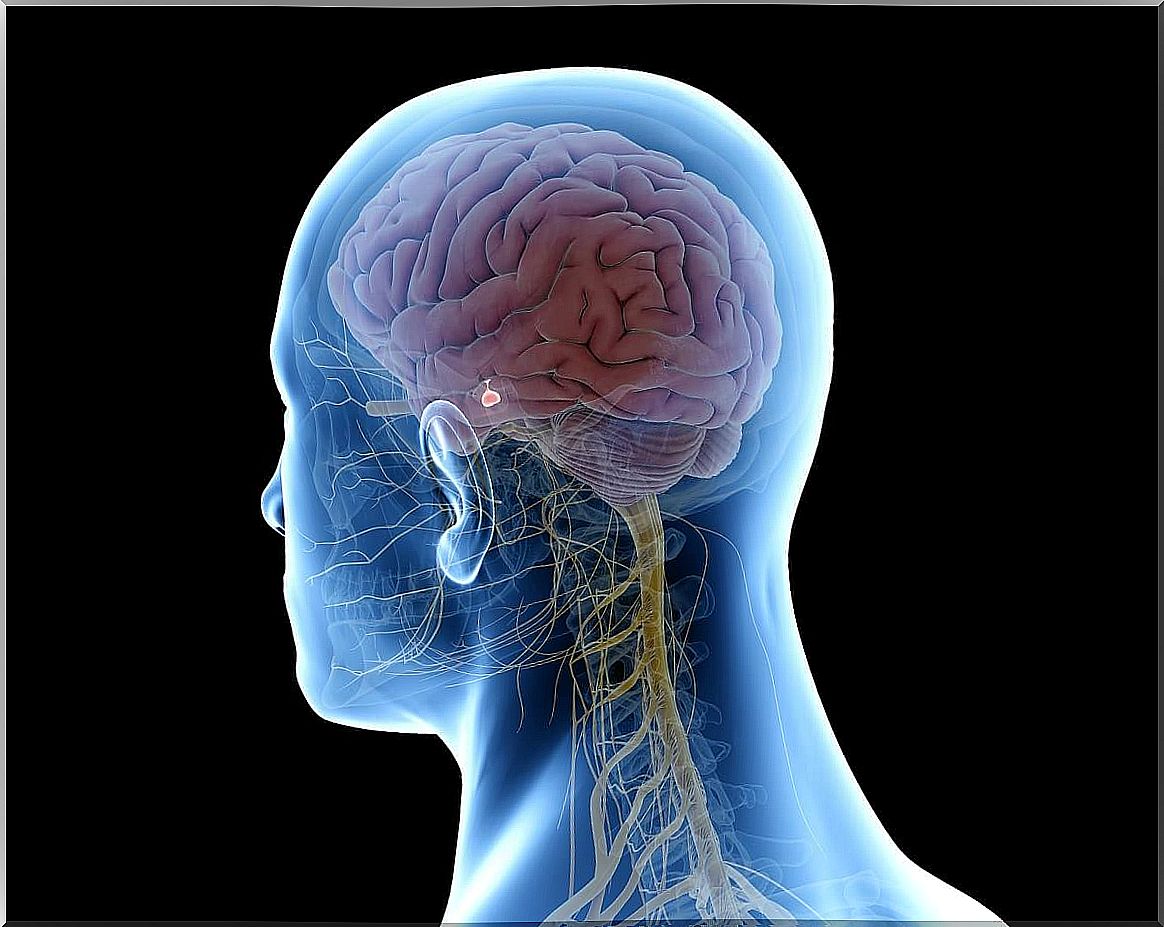
Tetraplegia is caused by damage to the brain or spinal cord; that is, in the central nervous system. This is in charge of regulating the executive functions of the human being that include, among others, muscle tone, motor control, movements, coordination and balance.
The first major component of the central nervous system is the brain. This includes the following:
- The cerebellum. It is responsible for coordination and balance.
- The brain stem. Regulates the nerves of the head, face, neck and part of the trunk.
- The brain. It is responsible for the control of movement, thought, emotions, personality, behavior, etc.
For its part, the spinal cord is responsible for transmitting messages to and from the brain. It is within the vertebrae; These are the bony discs that make up the spinal column. It is a network that carries incoming and outgoing messages between the brain and the rest of the body.
Why happens?
Quadriplegia is caused by damage to the spinal cord or brain. What happens in these cases is that the communication between these two structures is interrupted. Therefore, the body cannot process the signals to produce movement.
The damage originates from an injury or illness. In the case of injuries, as a general rule, those that occur in the cervical (neck) area tend to be more serious. Most of these injuries are caused by car accidents or falls.
Also, there are some diseases that result in tetraplegia. Among them are tumors, multiple sclerosis, Guillain-Barre syndrome, transverse myelitis, infantile cerebral palsy, spina bifida, stroke, and polio, among others.
Main symptoms
Generally speaking, the symptoms of tetraplegia are easy to identify. The most obvious manifestation is paralysis in the extremities and torso. Besides this, there may be other signs like these:
- Muscular weakness.
- Absence of voluntary movement.
- Atrophy.
- Lack of motor control.
- Anomalous reflexes.
- Loss or alteration of sensation.
- Lack of bladder, bowel, breathing, and digestion control.
- Alteration of sexual function.
At the same time, the inactivity caused by quadriplegia often leads to other problems such as pressure ulcers, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, weak bones, chronic pain and psychological difficulties.
Types of injury and tetraplegia
Most commonly, tetraplegia originates from a cervical spine injury. This area comprises seven vertebrae that are identified by the letter “C” and numbered from 1 to 7, from top to bottom. The injury in each one of them originates different effects. Let’s see.
- Lesion in C1 to C3. It corresponds to the vertebrae closest to the skull and those that cause the most serious effects. They almost always cause total paralysis.
- Lesion in C4. They cause severe limitation in the movements of the arms, legs and torso, in addition to loss of control in the diaphragm and urinary and fecal incontinence.
- Injury at C5. It usually causes paralysis in the legs, wrists and hands, as well as involvement of the vocal cords.
- Injury at C6. Paralysis in legs, hands and torso. Incontinence and difficulty speaking.
Lesions in C7 and lower vertebrae rarely lead to tetraplegia, unless there are other complications.
When tetraplegia originates in the brain, it is usually the result of spastic cerebral palsy that causes severe muscle weakness. Cerebral infarction also generates this type of paralysis, as do some accidents during childbirth.
Diagnosis
The most characteristic sign of tetraplegia is loss of mobility and sensation in the arms, legs, and torso. This motor impairment, noticeable in a clinical examination, is the usual way to diagnose this type of paralysis.
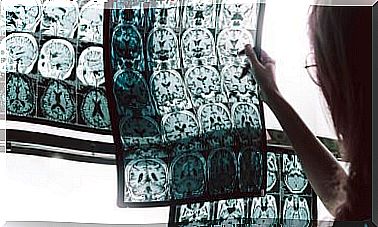
Rather, the diagnosis as such is aimed at establishing the cause and level of severity of the tetraplegia. To do this, imaging tests are commonly ordered to assess the condition of the spine and other structures. These tests can be a CT scan or an MRI.
In some cases, a myelogram or nerve conduction study is necessary to establish the condition of the muscles and nerves. Likewise, a lumbar puncture is sometimes used if there is suspicion of other neurological diseases.
Available treatments
The treatment to be applied depends on the causes of tetraplegia and the patient’s condition. It is aimed at maintaining vital functions, to regain control over the affected areas and to prevent possible complications derived from inactivity.
Typically, treatment includes a pharmacological component. Medications are given to maintain muscle tone, manage neuropathic pain, and, if applicable, address anxiety and depression.
In addition to this, it is usual to start a program of physical and occupational therapies so that the patient can lead a life as active as possible and without risks. Currently, the efficacy of stem cell therapy and nerve transfer surgery is being evaluated.
Recommended therapies
Most of the treatment of tetraplegia is carried out through various therapies. The most advisable are the following:
- Kinesitherapy. It seeks to keep the muscles strong and active, as well as to protect the joints. It allows to improve or recover the functionality of the affected areas.
- Physiotherapy. Its role is to strengthen the muscle. In addition, it allows the patient to learn to control it better and to be more autonomous. It mainly concentrates on the arms and hands.
- Respiratory therapy. It allows to strengthen the muscles associated with the airways and teaches the maneuvers and techniques to keep them clear.
- Electrostimulation. It is used to restore sensitivity and treat muscle atrophy.
- Occupational therapy. It allows to increase motor skills and gain autonomy.
- Neuro-psychotherapy. Offers emotional support and helps adopt healthy coping strategies.
- Others. A toilet training program is often required, as is skin care. There are also trainings and support for caregivers.
Recommendations you can follow
Quadriplegia involves a radical change in the life of the affected person and in that of those around him. The process of acceptance and adaptation can be very difficult, but it is important to carry it out in the best way to avoid difficulties and complications later.
The new life requires multiple changes and adaptations. Some of the most important are the following:
- Use of a wheelchair. This will be an essential element and the appropriate thing is that it works correctly and that it is of good quality. Ideally, it is the patient himself who chooses the one that best suits his tastes and expectations.
- Changes in furniture. It is necessary to rearrange the furniture, so that mobility in the wheelchair is facilitated. Barriers or risk elements must be removed. It is best to live on the ground floor and adapt a bathroom for the patient.
- Postural care. It is important to prevent pressure sores from forming. To do this, it is convenient to use elements such as cushions, ergonomic backrests, etc. Also, take care that the affected person changes position periodically.
- Catheter inspection. The catheter should be checked regularly to verify that it is in good condition and thus avoid urinary infections.
- Develop new interests. Life is going to change, but it doesn’t end. A person with quadriplegia can still develop new interests and activities. It is important to encourage him to do so, but also to give him time.
Family and medical support is essential
Although there is currently no cure for quadriplegia, there are currently several investigations in progress. It cannot be ruled out that partial or total solutions for this condition will emerge in the coming years.
Even without a cure, a person with this condition can improve their condition, sometimes very significantly, if they adhere to treatment with discipline and perseverance. Psychological help can be decisive for some people.