What Is Panniculitis?
Panniculitis refers to a group of conditions that involve inflammation of the subcutaneous fat. It can be classified as lobular or septal, according to its location.
Its main symptom is painful nodules or lumps under the skin, which are often located on the feet and legs. However, as detailed in an article published in The American Journal of Dermatopathology , its diagnosis is often difficult. Why is it produced? What are your symptoms? We will detail it below.
What Causes Panniculitis?
Most panniculitis have the same clinical appearance despite having very different causes. The many causes include the following:
- Infections (the most common).
- Autoimmune disorders (such as systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, etc.).
- Physical factors (such as trauma, exposure to cold, among others).
- Connective tissue disorders.
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AAT).
- Proliferative disorders.
You may be interested: Benign skin tumors: how do they manifest themselves?
Types of panniculitis
Sometimes the nodules can resolve spontaneously. However, this largely depends on the type of panniculitis. The most common include the following:
- Cold panniculitis : areas of the skin that have been exposed to low temperatures are altered.
- Indurated erythema : in this type the posterior region of the leg of middle-aged women is affected.
- Erythema nodosum : This is the most common form of panniculitis, according to studies by Dermatologic Clinics . Painful, red bumps develop on the front of the lower legs. In turn, it causes general symptoms such as headache, fever, and eye problems.
- Subcutaneous sarcoidosis: this variant is caused by the disease sarcoidosis
- Weber-Christian disease : idiopathic panniculitis (that which has no apparent cause) usually carries this name. It is the form of the disease that most often affects middle-aged women and causes nodules on the thighs and lower legs. In addition, it tends to alter other organs.
- Lipodermatosclerosis : is linked to obesity and varicose problems. It affects with greater prevalence overweight women, over 40 years of age.
Symptoms of panniculitis
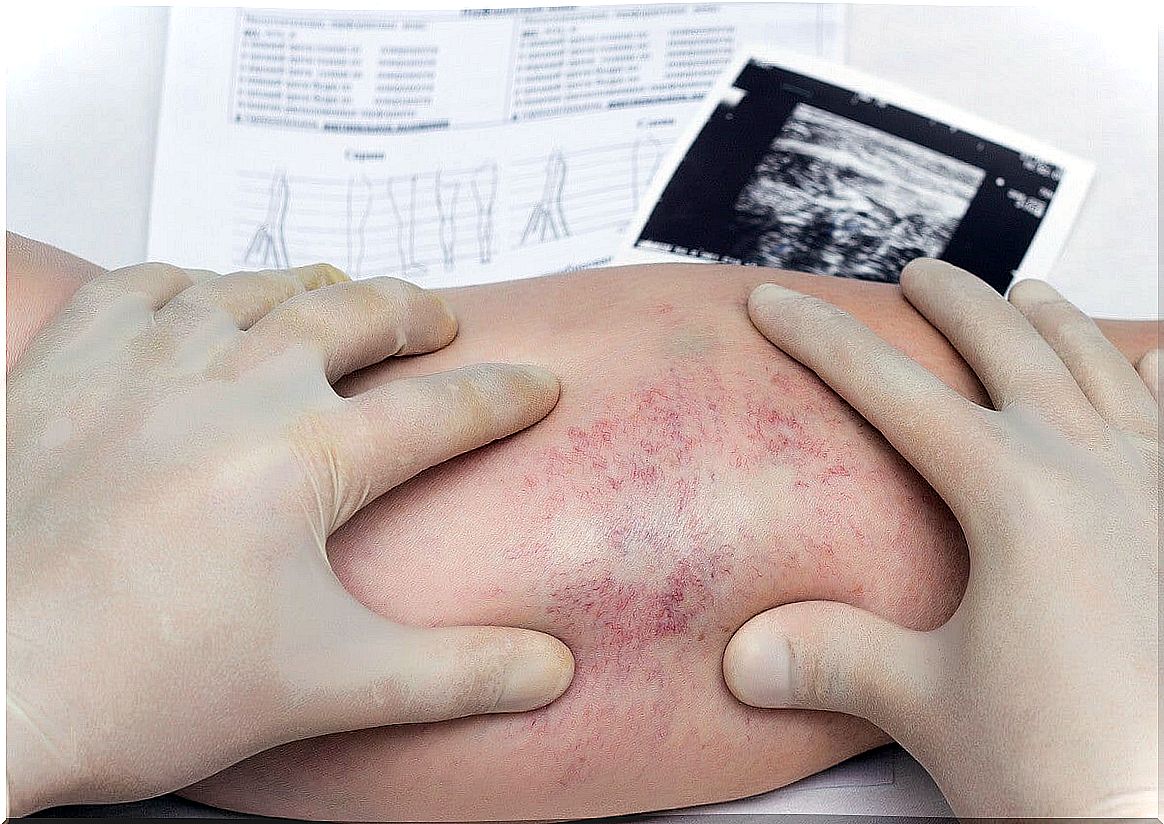
Panniculitis is characterized by the appearance of painful and erythematous nodules on palpation. In most cases they are located in the extremities; however, they can also appear in the abdominal area, back, face, buttocks or breasts.
In rare cases, the lumps involve other parts of the body such as the mesentery, scrotum, lungs, and skull. Signs of systemic inflammation may be found alongside panniculitis. In turn, it can manifest itself with other symptoms in the body such as the following:
- Fatigue.
- Fever.
- Weightloss.
- Abdominal pain.
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bulging of the eye
- Joint and muscle pain.
- Feeling generally unwell
Diagnosis of panniculitis
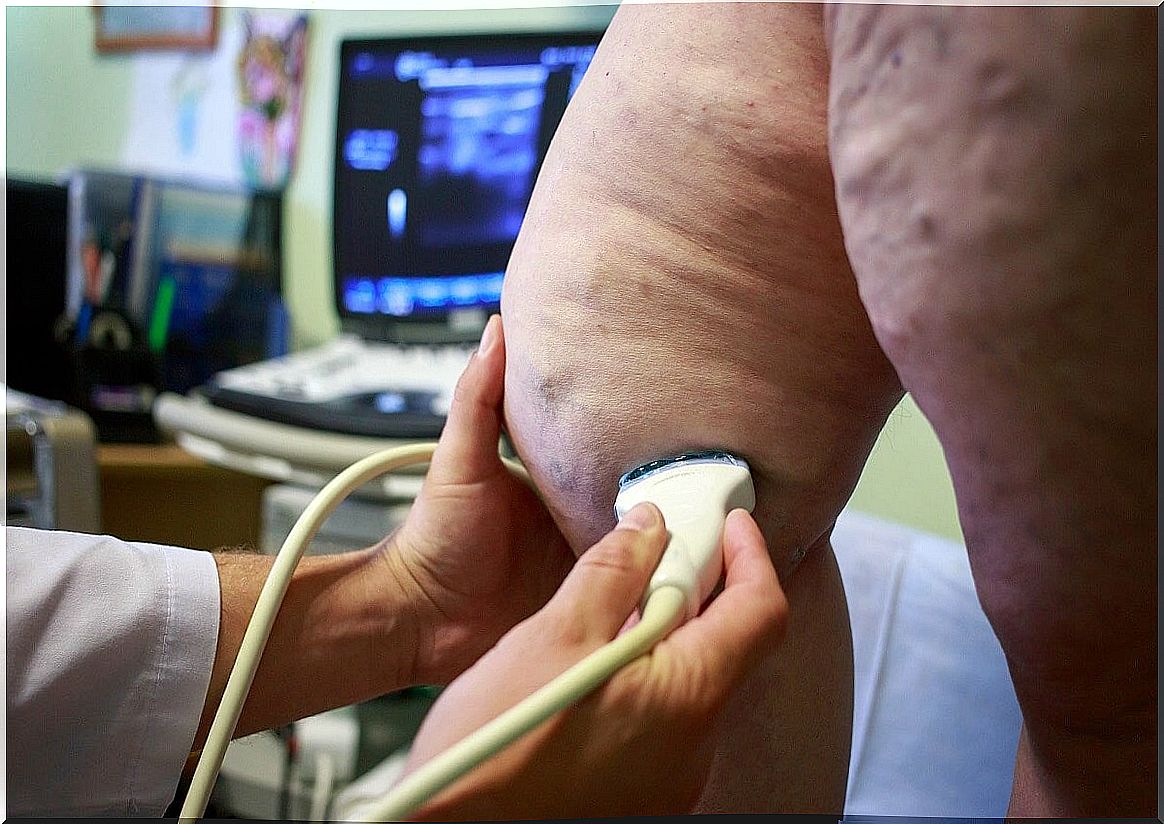
The diagnosis of panniculitis begins with a physical examination at the time of medical consultation, and is confirmed by taking a skin sample. Specifically, the doctor suggests an excisional skin biopsy, since there are characteristic microscopic features depending on the cause.
A review published in The American Journal of Dermatopathology concludes that the stage of evolution of a lesion at the time of biopsy significantly influences its microscopic appearance
Thus, histopathology shows whether the inflammation generated is septal, lobular, or mixed, with or without vascular damage. In turn, it is determined whether there is a predominance of neutrophils, granulomatous or lymphocytes.
What therapeutic options are there for panniculitis?
There is no specific treatment for panniculitis. Therefore, all underlying causes must be treated. The Revue de Medecine Interne suggests basing treatment on histopathological findings. The goal is to decrease inflammation and calm symptoms. Therefore, the indications are usually the following:
- Wear compression stockings.
- Rest and elevate the affected limb.
- Soothe pain with anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Decrease inflammation with oral or injected corticosteroids.
- Treat the underlying cause, if determined (for example, discontinue a drug, treat an infectious condition, etc.).
- Antibiotics with anti-inflammatory function including hydroxychloroquine or tetracycline.
What is the prognosis for panniculitis?
The prognosis of panniculitis will depend on the cause that generated the inflammatory condition. In fact, it can resolve spontaneously after you’ve had the injuries for a few weeks. However, it can come back over time.
Also, some of the variants of panniculitis leave lipodystrophy (localized subcutaneous atrophy). In any case, it is advisable to go to the dermatologist to receive a timely and appropriate treatment.