Juniper: Benefits, Uses And Contraindications
Juniper is a plant native to Europe, North America, and parts of Asia. Although it is famous for its uses as a condiment, it has also become popular for its medicinal applications.
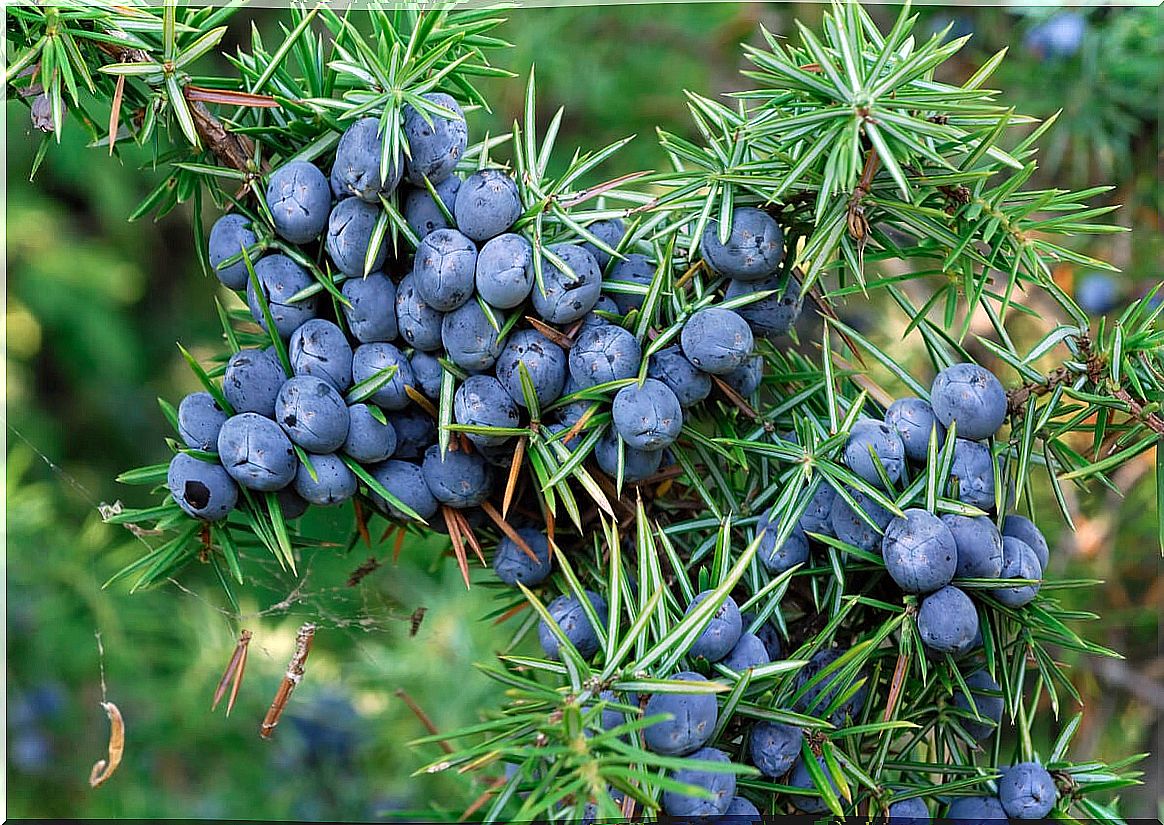

The juniper tree, whose scientific name is Juniperus communis , is a shrub native to Europe, parts of Asia, and North America. It belongs to the Cupressaceae family and it is estimated that there are between 60 and 70 species of its genus. It is also known as Juniperi fructus or “common juniper.”
Although it is often used as a flavoring for dishes and beverages, it stands out for its applications as a medicinal plant. And, as an article published in International Scholarly Research Notices exposes , it has antidiarrheal, astringent, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic activity. What are its benefits? In what cases is it contraindicated?
Juniper benefits
Juniper has been investigated in recent years due to its therapeutic potential against some diseases. And while the evidence is still limited, the findings are promising. An article published in the magazine Heliyon highlights that the plant contains substances such as the following:
- Aromatic oils.
- Inverted sugars.
- Resins
- Catechins.
- Organic acids.
- Terpenic acids.
- Leukoanthocyanidin.
- Alkaloids
- Flavonoids.
- Tannins
- Rubbers.
- Lignins.
- Waxes
Because of this, both its berries and extracts appear to be useful as nutraceuticals. In particular, they have shown positive effects as adjuvants against digestive problems, kidney diseases and infections. Let’s see its benefits in detail.
1. It has antidiabetic properties
In traditional medicine, juniper berries are considered a supplement to control high blood glucose levels. In this regard, a study in animals determined that supplementation with juniper berry lowered blood sugar and increased levels of good cholesterol (HDL).
Although other studies are necessary, the researchers suggest that these effects are due to the high antioxidant content of the fruit. For now, it should not be considered a first-line treatment for diabetes.

2. Helps promote heart health
In a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology , a juniper berry extract treatment was effective in reducing total cholesterol and triglycerides. Because of this, it is believed that it can be a supplement to improve heart health.
Both the flavonoids and other antioxidant compounds contained in the berries would be behind this effect. However, human studies are still lacking to prove it.
3. Has antibacterial and antifungal properties
Juniper has been noted for its antibacterial and antifungal compounds. According to an article published in Acta Pharmaceutica , these include sabinene, limonene, myrcene, and alpha and beta pinene. In particular, these substances showed efficacy against 16 species of bacteria, yeasts and dermatophytes.
A study published in Phytotherapy Research found that juniper berry extract helped fight bacteria like Campylobacter jejuni, which causes food poisoning. Meanwhile, other research has found that it can fight some microorganisms that cause respiratory diseases.
4. Supports digestive health
There is no evidence on the effects of juniper on digestive health. Still, anecdotal data suggest that it is a good supplement to stimulate gastric secretions and increase appetite. It even seems that it helps improve digestion in case of constipation.
5. Fight inflammation
A wide variety of chronic diseases cause increased inflammation in the body. In turn, this reaction leads to other ailments and complications that decrease the quality of life. In this regard, juniper is beneficial for its anti-inflammatory activity.
According to a publication in Cogent Medicine , essential oil, juniper berry proved useful to reduce inflammation in cells of human skin. This effect is attributed to its monoterpene and flavonoid content. In turn, this would be beneficial in controlling the symptoms of other inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis.
6. Other possible benefits
- Due to its vitamin C content, juniper helps to strengthen the immune system. In turn, it promotes collagen synthesis and protects against the negative effects of free radicals.
- It appears to have a diuretic effect that helps improve kidney function. In addition, it helps to calm the symptoms of cystitis.
- The plant is used in relaxing baths to reduce muscle tension and other stress-related ailments.
- Applied to the skin, juniper helps prevent infections and helps soothe problems such as dermatitis and excess oil production.
How is juniper used?
There are many ways to use juniper. In fact, due to its aroma and flavor, it is often used as a condiment in some dishes. It is also used in the liquor industry to enhance alcoholic beverages.
Now, for medicinal purposes the following forms are available:
- In tincture , up to 30 drops (2 milliliters) are consumed in water, 3 times a day.
- In infusion, incorporating 15 grams of juniper berries per cup of boiling water (250 milliliters). The drink is allowed to cook over low heat for 30 minutes and, later, it is consumed up to 3 times a day.
- For external massages , 10 drops of juniper oil are mixed in two teaspoons of carrier oil (almond, coconut or olive, in a quantity of 15 grams).

Juniper contraindications
Like many other natural remedies, juniper should be used with caution. Given the lack of evidence on its effects on human health, it should not be considered a first-line treatment when fighting diseases. Even before using it on a regular basis, it is best to consult your doctor.
Some of its contraindications are the following:
- Kidney diseases: its continued use can inflame the kidneys.
- Pregnancy: the plant stimulates the contractions of the uterus.
- Medical Treatments: Juniper supplements can interact with diuretic and psychiatric medications.
Juniper should be used sparingly
Despite being a natural remedy, juniper and its supplements are not without causing side effects. Therefore, it should be used sparingly and only in specific cases. Under no circumstances should it be a substitute for prescription drugs or therapies.
In fact, in case of illness it is better to consult a professional before consuming the plant or its derivatives. On the other hand, it is essential to ingest only the dose recommended by the manufacturer of the supplement. Keep that in mind!