Atrial Flutter, What Are Its Symptoms And Causes?
Atrial flutter is an arrhythmia; that is, a heart rhythm disorder. Also called atrial flutter . It consists of the production of abnormal and very fast electrical discharges in the atrium.
These shocks cause the atria to contract more quickly and, therefore, only some of these electrical impulses reach the ventricles. This causes them to contract in an irregular way, faster and less efficient than normal.
Atrial flutter is similar to atrial fibrillation. However, in flapping the rhythm is more organized than in fibrillation. It is a relatively common disorder, with a higher incidence in middle-aged men (60 years). Find out below what is atrial flutter, its symptoms and its causes.
How does atrial flutter occur?
Under normal conditions, as the MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia explains , the chambers of the heart (atria and ventricles) contract rhythmically and synchronously by an electrical impulse. This impulse is generated in the atrium and passes to the ventricle. In this way, the heartbeat is produced.
The normal rate is between 50 and 100 beats per minute. However, in an arrhythmia, this mechanism is disturbed. The heart stops contracting in that regular way. If the rate is greater than 100 beats per minute, it is called a tachyarrhythmia.
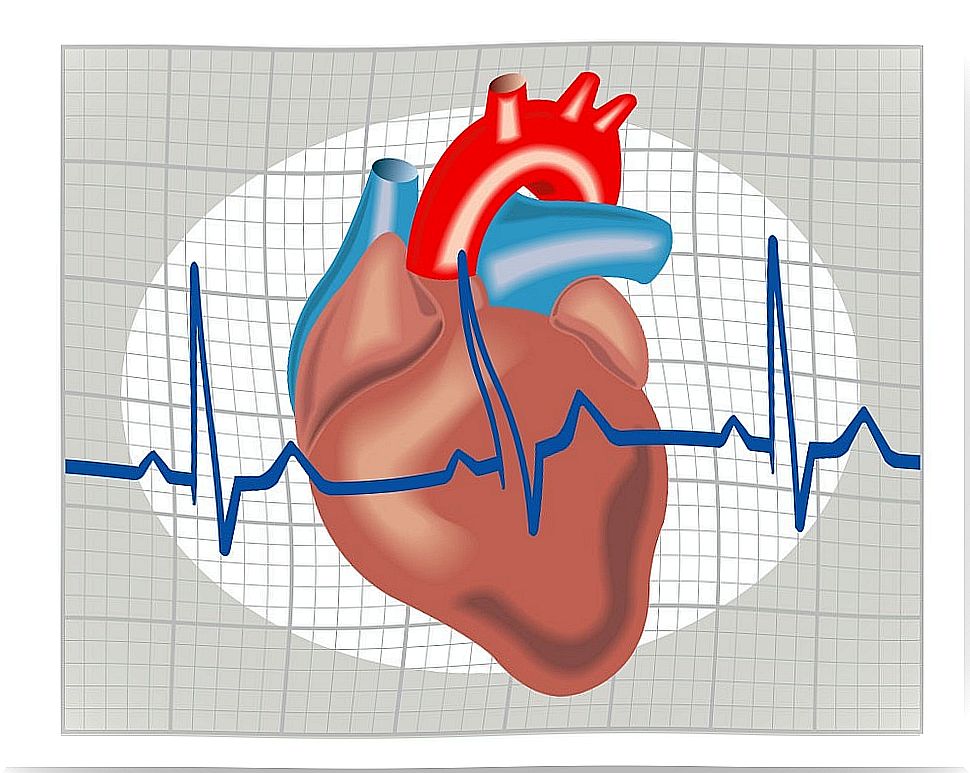 In the case of atrial flutter, the activity of the atria remains coordinated. The problem is that they contract at a rate of more than 250 times per minute. Therefore, the impulses cannot reach the ventricles correctly.
In the case of atrial flutter, the activity of the atria remains coordinated. The problem is that they contract at a rate of more than 250 times per minute. Therefore, the impulses cannot reach the ventricles correctly.
In fact, about one out of every two impulses reaches the ventricles. This causes a heart rate of about 150 beats per minute. In medical terms, atrial flutter is said to be a tachyarrhythmia produced by a macroreentrant circuit.
What are the causes of atrial flutter?
Atrial flutter is a common arrhythmia in patients with an underlying heart problem. For example, it is more common in people with hypertension, ischemic heart disease, or cardiomyopathy. However, it can also occur in people with a healthy heart.
An article from the MSD Manual of the year 2019 entitled Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter on this subject indicates that the main causes that cause this disorder are the following:
- Previous heart disease. Among them, heart valve diseases and coronary artery diseases stand out. In the same way, cardiomyopathies, which are alterations of the heart muscle, play a role.
- Hypertension .
- Alcohol consumption It has been associated, especially, with excessive consumption in a short time.
- Other diseases such as lung disorders or hyperthyroidism.
- Having suffered a previous myocardial infarction. It can also occur in people who have undergone coronary artery revascularization.
- Some medications
- Pericarditis
Symptoms of atrial flutter
The symptoms will depend on the speed at which the ventricles contract. This speed causes the heart’s ability to pump blood to decrease. In fact, symptoms can start or stop suddenly.
L. Brent Mitchell, MD of the Libin Cardiovascular Institute of Alberta at the University of Calgary explains that the most typical symptoms are dizziness and shortness of breath. Other symptoms are:
- Weakness.
- Palpitations
- Confusion and / or fainting.
- Fast, throbbing and irregular pulse.
- Loss of ability to exercise.
- Chest pain, especially in those with other heart problems.
Also, atrial flutter can be complicated by blood clots in the atria. This can be caused because, by beating so fast, the atria do not empty completely and the stagnant blood ends up forming clots.
Also, fragments of the clot can break off and travel through the bloodstream. If these fragments block an artery, they can cause ischemic problems in another area of the body. For example, pulmonary thromboembolisms or strokes.
How is it diagnosed?
The doctor will first listen to the heart and measure the heart rate. Diagnosis is usually based on rate, symptoms, and the EKG.
However, atrial flutter can be intermittent. For this reason, there are other methods that record heart rhythms over a longer period of time. They stand out:
- Event monitor (3 to 4 weeks)
- Holter monitor (24-hour exam)
- Subcutaneous implantable recorder (extensive monitoring)
Furthermore, as we have mentioned, atrial flutter usually occurs in patients with underlying heart disease. For this reason, tests such as echocardiography and angiography are often performed . Similarly, blood tests are carried out, in which the doctor also assesses the activity of the thyroid.
See your doctor if you have symptoms
Atrial flutter is a relatively common heart rhythm disorder. Therefore, it is necessary to know its symptoms and go to the doctor before any alarm.
In conclusion, if you feel weakness and palpitations, a racing pulse and chest pain, do not hesitate and approach your cardiologist so that he can examine you and provide you with a timely diagnosis and treatment. In this way, possible heart problems can be avoided.