Diabetic Eye Problems: What You Should Know
Elevated blood glucose is a condition that affects various systems and organs. And he does it silently. One of the most important aspects related to this pathology is diabetic eye problems.
The cardiovascular impact of diabetes is often discussed, but the impact it has on vision is not emphasized enough. Diabetic eye problems can lead to total blindness. In addition, the vast majority are associated with poor control of the clinical picture.
Why do diabetic eye problems occur?
Diabetes is a chronic disease related to glucose (sugar). What happens is that the pancreas cannot synthesize enough insulin or the tissues are not able to use it correctly.
Insulin is the key that allows glucose to enter cells. When it fails, the substance dramatically increases its concentration in the blood. This causes the tissues to be damaged. According to experts from the Mayo Clinic, diabetic eye problems occur because high glucose levels, maintained over time, damage the blood vessels of the retina.
Diabetes is considered a silent disease that, if neglected, can lead to serious complications. In fact, as the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases points out , symptoms are often associated with a change in medication or care for the disease.
However, long-term damage begins even during prediabetes. It is a period in which glucose levels are higher than normal. However, they are not high enough to establish the definitive diagnosis of diabetes.

Main diabetic eye problems
Diabetic eye problems encompass all those that appear as a result of this disease. The most common are diabetic retinopathy, macular edema, glaucoma, and cataracts. We explain what each of them consists of.
Diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that is caused by damage to the blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to the retina. The retina is the light-sensitive part of the eye at the bottom of the eyeball.
Retinopathy is one of the most common diabetic eye problems. It usually takes place in stages. As explained by the American Academy of Ophthalmology , the first part is non-proliferative retinopathy.
What happens is that the blood vessels begin to weaken or leak into the retina. At this time, macular edema occurs and blurred vision is common. In some cases it can lead to ischemia of the blood vessels.
As retinopathy progresses, it reaches the proliferation stage. It consists of the formation of new vessels (this process is also called neovascularization or angiogenesis ). These vessels are weak and can be injured and bleed.
Bleeding impairs vision. Additionally, scar tissue can form, making the inside of the eye increasingly opaque. Therefore, the light cannot correctly reach the retina.
Diabetic macular edema
Macular edema is another common diabetic eye problem. In fact, as we have seen in the previous section, it usually appears in retinopathy. It occurs when fluid builds up around the macula and inflammation occurs.
The macula is the central part of the retina. It is what allows the vision to be detailed and also for the central vision to exist. This is why diabetic macular edema can lead to loss of vision or even blindness over time.
Glaucoma
Another of the diabetic eye problems is glaucoma. It is a situation that is produced by an increase in pressure inside the eye. What happens is that the drainage system is disturbed and the fluid accumulates.
This causes the optic nerve to be damaged little by little. As explained by the Mexican Diabetes Federation, glaucoma is considered the second cause of blindness in general and the first of irreversible blindness.
Diabetes doubles the chances of suffering from this pathology compared to a healthy person. Symptoms usually appear progressively and vision is gradually lost.
waterfalls
Cataracts are a pathology that, in healthy people, is also common and is associated with aging. It is a process of wear and tear in which the lens becomes increasingly opaque.
This causes the vision to be less clear. It is considered another of the diabetic eye problems because diabetes causes this to accelerate. That is, people with diabetes develop cataracts at a younger age than the rest.
When should you consult a specialist?
Diabetic eye problems do not usually show symptoms until the damage is quite advanced. That is why it is considered essential that anyone with diabetes undergoes comprehensive examinations on a routine basis.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), almost all diabetic eye problems can be prevented. To do this, it is essential to detect the alteration early and begin to strictly control blood glucose levels.
It is recommended that all people diagnosed with diabetes have tests, such as the fundus, at least once a year. It is also essential to check more frequently if that person has hypertension or high cholesterol levels.
The greatest risk of diabetic eye problems is having high blood glucose consistently. That is why it is essential that diabetics keep strict glycemic control throughout the day. This is how the treatment is adjusted to avoid these peaks.
What we must remember is that, once diabetes or prediabetes has been diagnosed, medical consultations and controls are essential. You do not have to wait for symptoms or complications to go.
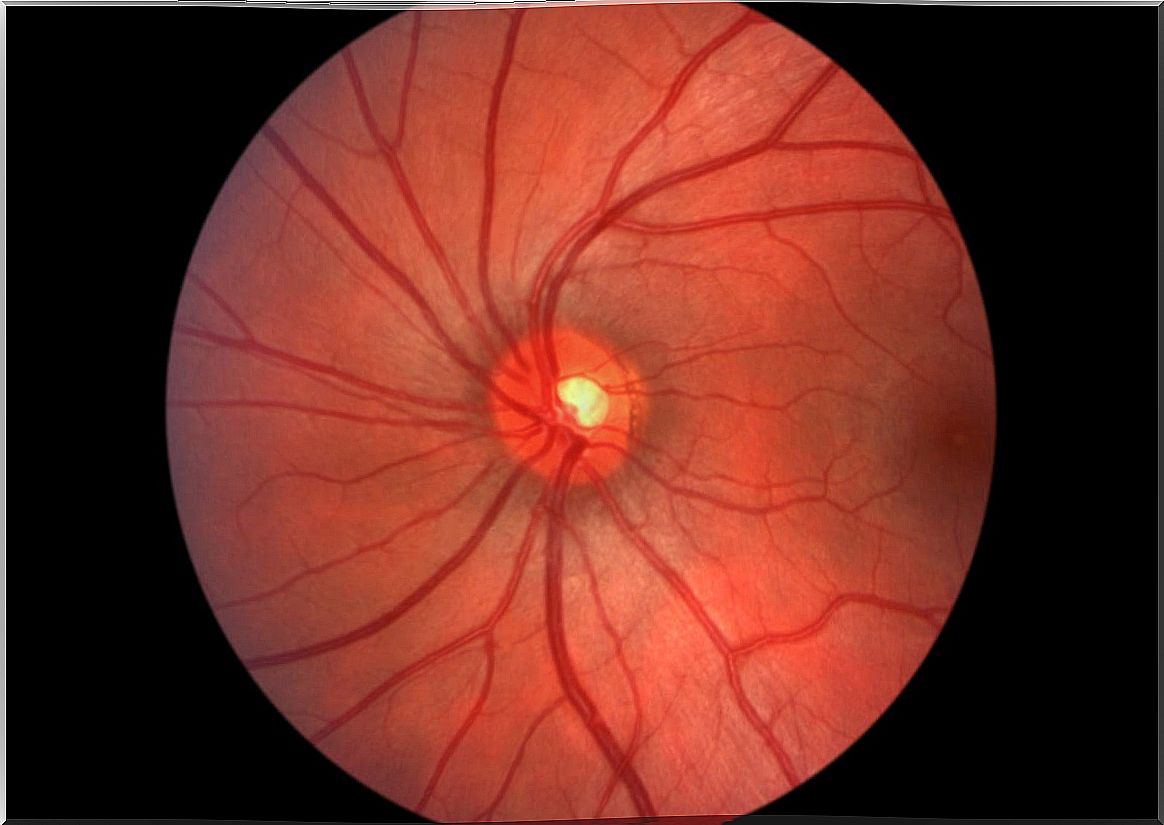
Treatment of diabetic eye problems
In the case of diabetic retinopathy, drugs can be used in the early stages. The most used are anti-VEGF and corticosteroids. The former are injected into the eye and reduce the proliferation of blood vessels around the retina. In addition, they also reduce macular edema.
Corticosteroids are responsible for controlling the swelling of the edema. However, there are cases that do not respond and require surgery. As explained by the Hospital Clinic de Barcelona, there are three main indications:
- Very dense or recurrent vitreous hemorrhage.
- Macular edema that does not respond to treatments.
- Retinal detachment.
Diabetes is a silent disease
Diabetic eye problems are the result of poor glycemic control, especially in people who have been diagnosed with diabetes for many years. The most important thing to highlight about these pathologies is that most of them are avoidable.
For this reason, it is essential to go to the medical controls that are carried out on a semi-annual or annual basis. In addition, trying to follow all the recommendations on diet and lifestyle are basic aspects to reduce the incidence.