Entomophagy: Know The Main Edible Insects
Insects represent the largest and most widely distributed animal group on the planet. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), entomophagy or feeding with insects is ancestral for countries in Asia, Africa and Latin America.
On the other hand, the increase in the world population generated great challenges on food security. Currently, the demand for food is increasing to satisfy hunger and reduce malnutrition. According to Patel, the consumption of the Insecta class is presented as a short-term alternative.
Insects provide up to 80% protein when baked, fried or roasted. Also, they are the only animal-based foods that contain fiber. So, do you dare to know more about the main edible insects in the world?
Why eat insects?
There are several reasons that justify entomophagy as part of the usual diet of the general population. Let’s review what they are.
Safe sourcing
The FAO and the European Union (EU) assure that entomophagy is a favorable solution to satisfy the high demand for food worldwide. Pulido and other researchers point out in the journal Advances in Agricultural Research that insects represent the largest amount of mass estimated as a biological group on earth. In addition, they reproduce rapidly and are in all environments, with more than 1,000,000 species recorded.
Nutritional attributes
There are many nutrients that insects provide. Highlights, for example, the richness in protein, which thanks to its short life cycles is synthesized quickly. The rest of the nutrients depend on the species. In general, those most consumed have nutritional attributes greater than other food sources, such as pork, poultry and cattle.
Development prospects
FAO established some programs, such as Edible Insects for the Sustainability of Safe Food in the World. It is estimated that by 2050 there will be 9 billion people inhabiting the planet, so food production must be doubled. Currently, 1 in 3 inhabitants of the world consume insects in their diet.
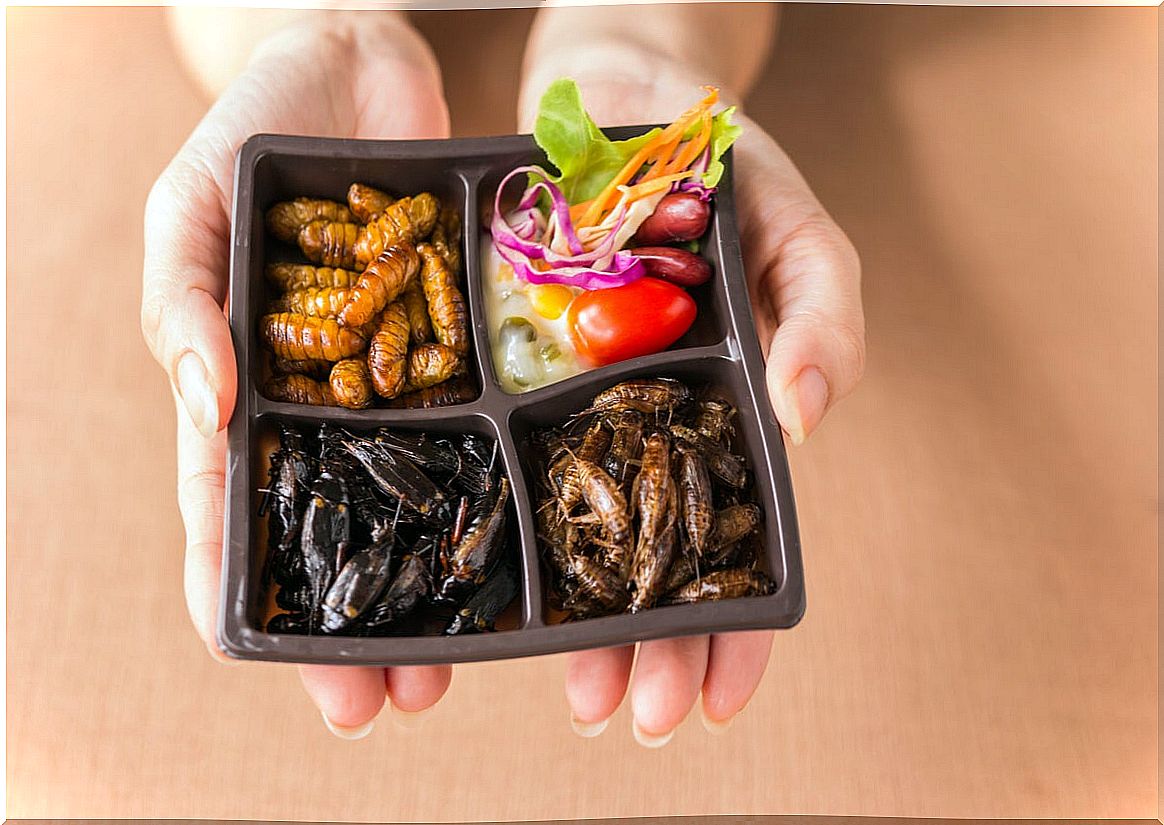

Sustainability of entomophagy
One of the most important aspects of entomophagy is sustainability compared to traditional livestock. Insects, for example, can be raised in a higher density of soil. According to Dzamba, 64 kilograms of insects can be produced per cubic meter, compared to 0.13 kilograms per square meter of beef.
Insects can be fed with plant debris from the human diet or plants not used by man. In addition, they are more efficient at converting food into body mass, with the amount of net food produced by an insect being 12 times greater than that produced by livestock.
Where is entomophagy usual?
The 2,100 species of insects that are consumed are distributed in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. The main places where the insect is the dish of the day are Asia, Africa and Latin America. In the United States, restaurants for tasting insects are beginning to appear and in the European Union it is a very incipient market.
China, Japan and Mexico are the 3 countries that practice entomophagy in the highest proportion. In Mexico there are more than 600 species of insects that are part of the gastronomic culture of this country. While in Africa 470 species are consumed and in China 324.
Main edible insects
The insects that are mainly consumed in the world appear in the following table. The most consumed are the beetles and the caterpillar. Dragonflies, termites and flies are the least eaten.
| Species | Common name | % of consumption |
| Beetles | Beetle | 31 |
| Lepidoptera | Caterpillars | 18 |
| Hymenoptera | Bees, wasps and ants | 14 |
| Orthoptera | Grasshoppers, locusts and crickets | 13 |
| Hemiptera | Fulgoromorphs, leafhoppers, mealybugs, and bed bugs | 10 |
| Isoptera | Termites | 3 |
| Odonates | Dragonflies | 3 |
| Diptera | Flies | two |
| Other orders | Others | 5 |
Some insects in world gastronomy
There are hundreds of culinary techniques, cookbooks, online recipes, and restaurants specializing in insects. Chef David Gordon wrote the bestseller “Eat-a-Bug Cookbook” featuring different insect preparations around the world. Some that are part of interesting recipes are the following:
- Thai cricket – eaten as a snack and is a true delicacy in Thailand.
- Agave worm in Mexico : it is prepared grilled or fried and accompanied with some condiments or hot sauces.
- African cicadas : with a flavor similar to almonds, they are usually eaten toasted.
- Culona ants from Colombia : they are used as a delicious snack and have a flavor similar to peanuts.
- Chapulines de México : they have a very attractive flavor, similar to chicharrón, and are eaten stewed or toasted accompanied by various sauces.
- Peruvian Suri : the indigenous people of the Amazon eat it directly from the tree or roasted.
- Peruvian Siqui Sapa : These ants with a large abdomen have a somewhat rigorous preparation. They are first cleaned and roasted until completely free of moisture. Then they are fried with salt and butter.
Benefits of entomophagy
Insects have a higher protein content than beef, pork, beans, and soybeans. They contain essential amino acids, such as lysine and leucine, which supplement the cereal-based diet of many peoples.
They provide as much fat as pork and the most caloric are termites and caterpillars. Quirce points out, in Biodiversity Notebooks, that the cholesterol content is lower than that of traditional meat, but more research is still required on this component. They also have more omega 3 and omega 6 polyunsaturated fat.
Insects contain a type of fiber called chitin. It is a component absent in the rest of the foods of animal origin. Its values are close to that of cereals, with almost 10%. They are a good source of B vitamins and minerals such as phosphorus, magnesium, and iron.
The silkworm covers almost 200% of the recommended daily amount of iron (18 milligrams%), 70% of phosphorus (1%) and 153% of zinc (15 milligrams%). Termites cover more than 100% of the recommended for magnesium (400 milligrams) and 680% for copper (2 milligrams%).
Contribution to health
According to the FAO, there are no reports of parasites to humans through the consumption of insects, as long as hygiene standards are respected. In addition, the consumption of insects reduces the transmission of zoonotic diseases, such as bird flu and mad cow disease. This would have a positive impact on public health.
The biologist Georgelin Espinoza also refers that entomophagy benefits the immune, bone and nervous systems and repairs cells and tissues. In addition, it increases digestibility and improves intestinal transit due to the high fiber content.

Environmental contribution
Insects use less water than traditional livestock. In addition, they emit less greenhouse gases, such as ammonia. They can feed on waste, manure and compost to transform it into protein. It is an ecological way of cultivation.
Main cons of entomophagy
The main barrier to the insect industry is achieving consumer acceptability. Today it is difficult to include insects as part of a regular diet, especially in Western culture. In a study conducted by Hartmann it was concluded that the high benefits provided by insects do not impact on who consumes them.
For example, ants and cockroaches are rich in protein, but their taste is highly rejected. Although they are combined with sauces, curries, chocolate and other condiments. Work is being done to improve the flavors and textures of insect-based preparations.
Other disadvantages of using insects for food is that some produce methane gas, which pollutes the environment. They can also cause allergies, so you have to be vigilant.
Without a doubt, insects represent great potential for human consumption. This is why international organizations support its development as a food safety product. However, it is necessary to break down some cultural barriers that facilitate their inclusion in the usual diet.