Is Leishmaniasis Contagious?
Leishmaniasis is an important disease, contagious in its own way, as we will see, that generates a great public health problem. It appears frequently in 88 countries of the world, including Spain. It affects 14 million people globally, with 2 million new cases each year.
Despite being considered one of the seven most important tropical diseases globally, leishmaniasis is a very neglected and forgotten disorder. In Spain, according to a study by the National Epidemiology Center, between 2014 and 2017 there were 1,359 autochthonous cases spread over 15 autonomous communities.
What is leishmaniasis?
Leishmaniasis is a contagious infection produced by different species of protozoa of the genus Leishmania . These protozoa, also called parasites, are microscopic organisms that need a vector to be transmitted.
A vector is an animal that transmits pathogens from an infected person or infected animal to a healthy person. In other words, the disease is not spread by direct contact, but there is a second organism that carries the microorganism.
In general, these vectors are usually invertebrates, such as mosquitoes, fleas, lice and ticks. In the case of the pathology we are describing, the Leishmania protozoan is transmitted by the bite of the sand fly mosquito .
The mosquito becomes infected when it ingests blood from an infected person or animal. Once inside, the parasite does not cause any symptoms to the vector; it just develops and divides.
When there are a sufficient number of parasites, they go to the mouth and pharynx of the mosquito, to be injected at the next bite. The infected sand fly bites another human or animal, injects it with Leishmania and contagion occurs .
Despite the defense of the human body, the pathogen does not die. Rather, it reproduces inside macrophages in the blood and tissues, which end up breaking down and releasing protozoa into the blood, where other macrophages become infected and the cycle continues.
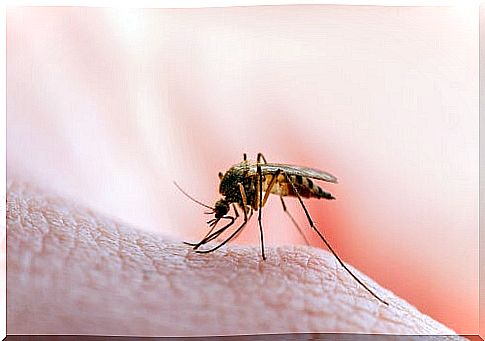
Where are these vectors found?
The sand fly loves humidity and heat, therefore we will find it in tropical and subtropical areas. However, it also inhabits the Mediterranean basin.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), leishmaniasis is an infection that is linked to environmental changes and has the following risk factors among its risk factors:
- Socio-economic conditions: Poverty increases the risk of leishmaniasis, as it implies poor housing conditions and poor household sanitation. This promotes the breeding and resting development of the transmitting mosquitoes.
- Malnutrition: the deficit of proteins, iron, vitamins and minerals, causes that the person does not have a good defense system, allowing the disease to advance and spread.
- Population mobility: population settlements in former wooded areas, which are the habitat of the mosquito, lead to a rapid increase in cases.
- Environmental changes: deforestation, construction of dams, irrigation systems and urbanization, cause mosquitoes to have more contact with humans.
- Climate change: the Leishmania is very sensitive to changes in climatic conditions. Variations in temperature and humidity in different areas make mosquitoes migrate to places where they did not previously inhabit.
What are the symptoms of leishmaniasis?
There are at least 20 species of protozoa of the genus Leishmania that can be transmitted by vectors. Depending on the species and its degree of invasion in the body, we can present some symptoms or others, establishing different varieties of the pathology.
The three common ways are as follows:
- Cutaneous leishmaniasis : Cutaneous leishmaniasis occurs when the infection is limited to the area of the bite. It is also known as the Eastern button and it usually appears on the Mediterranean coast. At the site of the bite, a lesion appears as an ulcerated protrusion, which sometimes heals spontaneously, leaving a scar.
- Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis: the parasite can spread from the skin to the mucous membranes, especially affecting the upper respiratory tract. It occurs with swelling, redness and ulceration of the mucous membranes.
- Visceral leishmaniasis: in addition to the type of infecting protozoan, the immunity of the infected person must also be taken into account. When the defense system fails, the parasite can migrate into the viscera. The internal organs most affected are the bone marrow, lymph nodes, liver, and spleen.
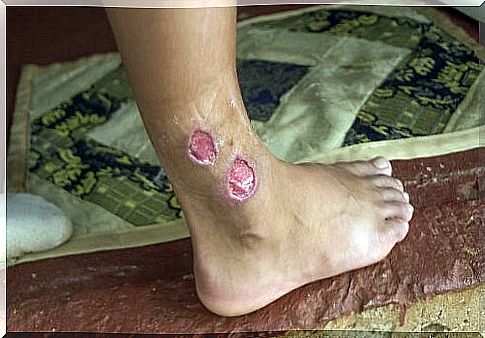
How can I prevent the spread of leishmaniasis?
Leishmaniasis is contagious as long as the vector exists. It cannot be asserted that there is human-to-human transmission, except for specific cases that have been recorded, for example, with people who share syringes to inject drugs. On the other hand, blood transfusions are totally safe, since they go through many controls.
However, it is worth thinking that in a place where there are infected people, there will be more infected mosquitoes, and that will increase the probability that people around you will be infected. Speaking of leishmaniasis as a contagious disease is possible, provided that we consider the participation of the vector.
Therefore, the main prevention begins with avoiding mosquito bites, especially in people who travel to countries where the disease is common. Good tips to follow to avoid bites are the following:
- Use insect repellants on exposed skin.
- Wearing mosquito nets on clothing and treating clothing with medications, such as permethrin.
- Wear socks, long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and tucked-in shirts to prevent mosquitoes from accessing the skin.
- Avoid outdoor activities from dusk to dawn in tropical areas, which is when mosquitoes are most active.