Oxytocin
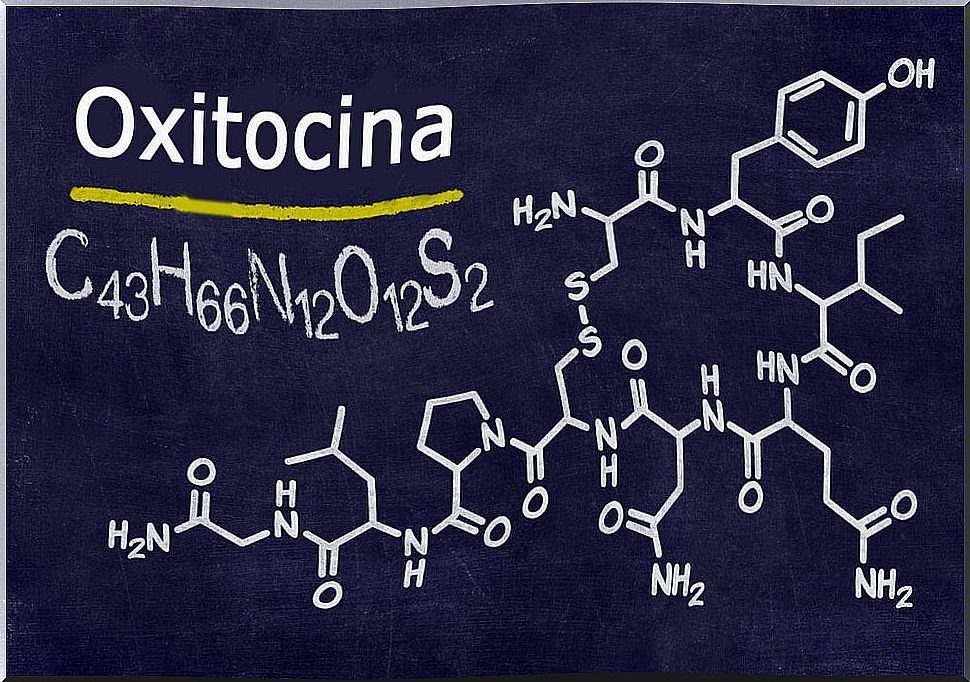
Oxytocin is considered the main hormone in labor and lactation. Its structural conformation is of 9 amino acids which include: cysteine, tyrosine, isoleucine, glycine, proline, asparangine, cysteine, leucine and glycine. It is produced in the posterior pituitary, and participates in different physiological processes.
Its chemical composition is similar to that of its complementary, vasopressin, which is produced in the anterior pituitary. Oxytocin has several receptors which are found mainly in:
- Uterus.
- Kidney.
- Bone.
- Heart.
- Brain.
- Ovarian tissue.
- Mammary glands
Due to the processes in which it participates, oxytocin is considered the maternity hormone.
What actions does oxytocin mediate?
Reproduction
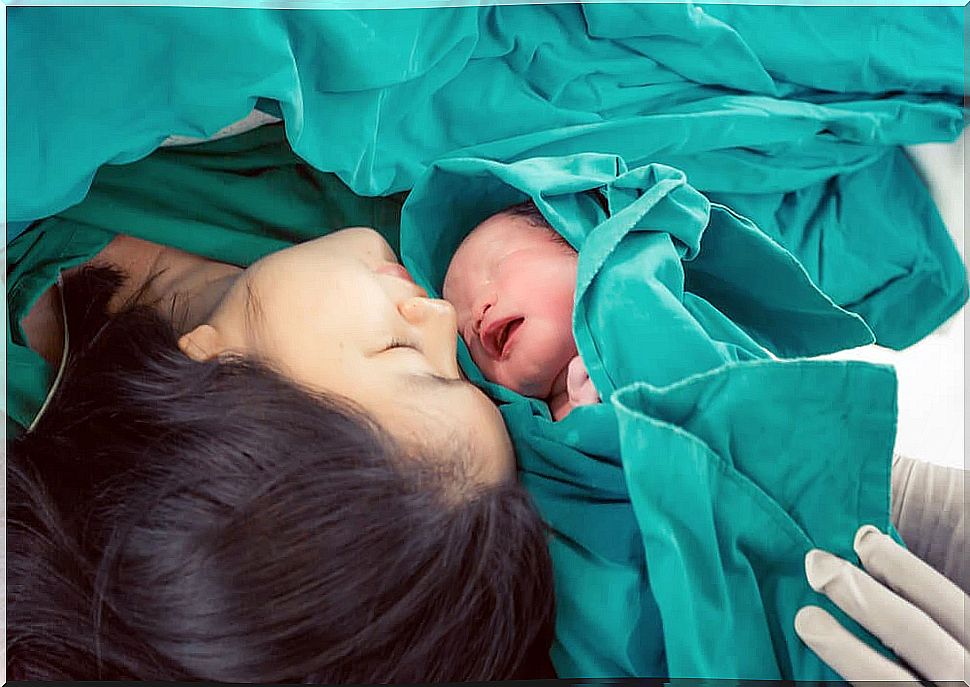

This hormone is responsible for inducing and advancing labor more quickly. E l organism releases high amounts of oxytocin causing uterine contractions. In this way, the baby’s passage through the canal and neck is facilitated. These amounts increase if the woman’s nipples are stimulated.
In the male reproductive system, this hormone acts directly on the erectile tissue, both in the corpus cavernosum and in the corpus spongiosum, which is why it is associated with ejaculation through the ejaculatory duct and urethra.
Mammary glands
Oxytocin also causes contractions in the myoepithelial cells of the mammary gland, which facilitates the suction of milk by the newborn.
Renal System

Urine retention caused by oxytocin is related to molecular events in the basolateral canals of the kidney. This antidiuresis with symptomatic hyponatremia occurs more frequently in pregnant women who have been induced to labor with oxytocin.
Labor
The indications and receptors for oxytocin in the uterus depend on the amount of the hormone present in the body. In the early stages of labor, it is recommended to start the dose between 1 to 6 mU / min and increase it over a range of 15 to 60 minutes.
This promotes the hormonal affinity of the receptors, which improves contractions for active labor.
Postpartum hemorrhage

Postpartum hemorrhage is considered to be bleeding of uterine origin that exceeds 500 ml, and from 1000 ml it is considered serious. It is more common in cesarean deliveries. Uterine atony is responsible for bleeding in 80% of cases.
Maternal relationship
The relationship between mother and child is strengthened thanks to oxytocin. This hormone causes amnesia of the pain experienced during labor, which makes you feel no fear of reproducing again.
Side effects of oxytocin
Oxytocin, especially synthetic, can cause some adverse effects, including:
- Arterial hypertension.
- Sudden mood swings.
- Tachycardia in mother and fetus.
- Abnormal contractions after delivery.